Description
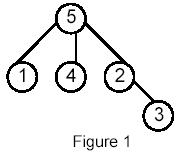
Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree description, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 … successorn
…
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) …
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1
5:5
题意
给出一棵树,有 n 次查询最近公共祖先,输出所有查询所涉及到顶点的次数,未涉及则不输出。
思路
标准 LCA 问题,使用离线 tarjan + 并查集实现,在遍历过程中记录所有查询到的公共祖先出现次数即可。
AC 代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1001;
int fa[maxn];
int rank[maxn];
int indegree[maxn]; //入度
bool visit[maxn];
vector<int> tree[maxn],Qes[maxn];
int ancestor[maxn];
int ans[maxn];
void init(int n)
{
memset(rank,0,sizeof(rank));
memset(visit,false,sizeof(visit));
memset(indegree,0,sizeof(indegree));
memset(ancestor,0,sizeof(ancestor));
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
fa[i]=i;
tree[i].clear();
Qes[i].clear();
}
}
int find_set(int x) //并查集 查询+路径压缩
{
if(x!=fa[x])
fa[x]=find_set(fa[x]);
return fa[x];
}
void union_set(int x,int y) //并查集 合并
{
x=find_set(x);
y=find_set(y);
if(rank[x]>rank[y])
fa[y]=x;
else
{
fa[x]=y;
if(rank[x]==rank[y])
rank[y]++;
}
}
void LCA(int u)
{
ancestor[u]=u;
int len = tree[u].size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
LCA(tree[u][i]);
union_set(u,tree[u][i]);
ancestor[find_set(u)]=u;
}
visit[u]=true;
len = Qes[u].size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
if(visit[Qes[u][i]]) //如果该点之前访问过,输出最近公共祖先
ans[ancestor[find_set(Qes[u][i])]]++;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
init(n);
int now,son,num;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d:(%d)",&now,&num);
for(int j=0; j<num; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&son);
tree[now].push_back(son);
indegree[son]++;
}
}
int ci,u,v;
scanf("%d",&ci);
for(int i=0; i<ci; i++)
{
scanf("%*[^0-9]%d%d)",&u,&v);
Qes[u].push_back(v);
Qes[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(!indegree[i])
{
LCA(i);
break;
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
if(ans[i])
printf("%d:%d\n",i,ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}